The role of efficiency in enhancing manufacturing processes
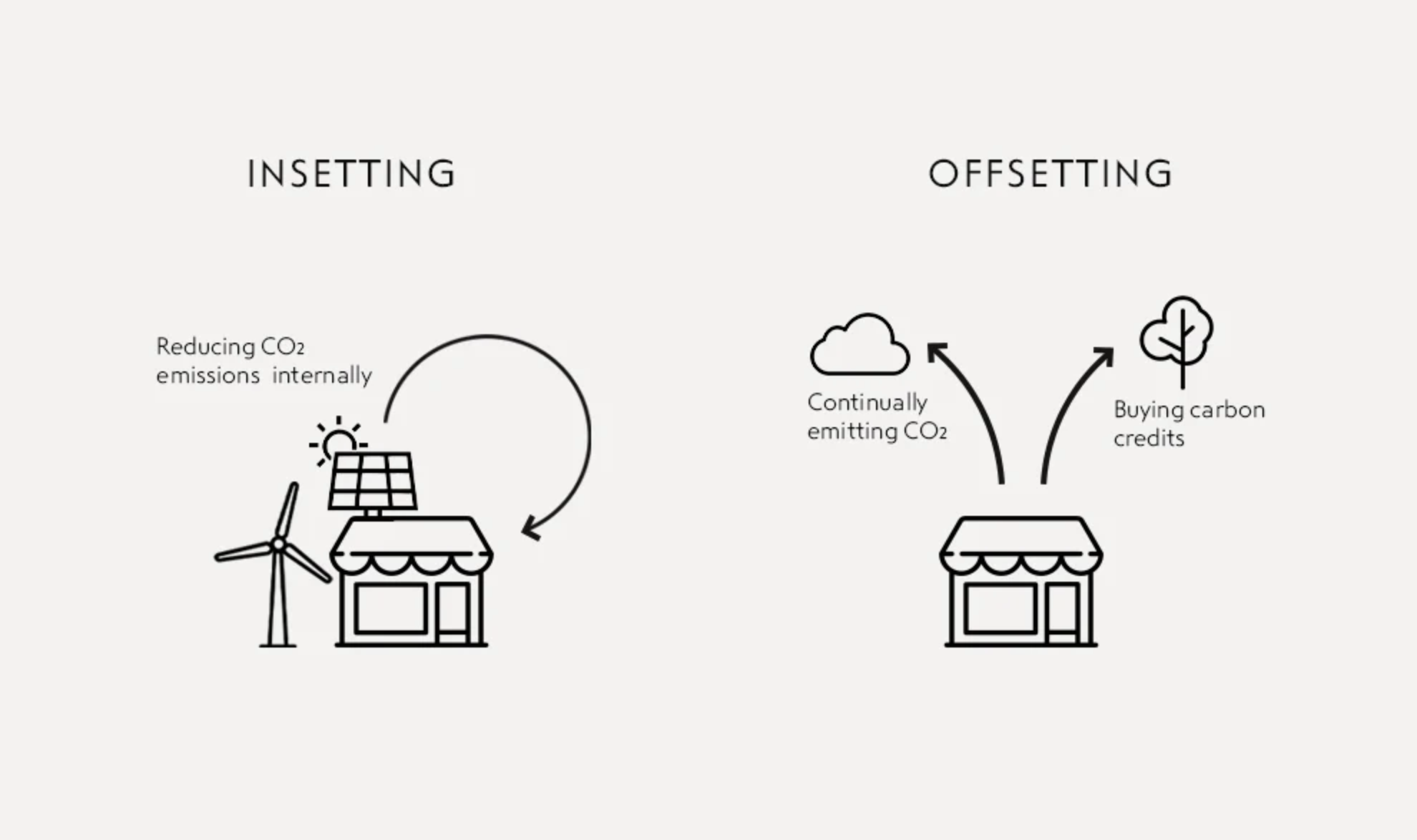
The Difference Between Carbon Insetting and Offsetting
In the world of environmental sustainability, two terms often come up: carbon insetting and carbon offsetting. While they both aim to reduce carbon footprints, their approaches differ.
- Carbon Offsetting involves compensating for emissions, by funding external projects that reduce greenhouse gases.
These might include reforestation or renewable energy initiatives.
- Carbon Insetting, on the other hand, focuses on reducing emissions within a company’s own supply chain.
This is more about direct action, like improving energy efficiency or adopting cleaner technologies in-house.

In sustainability narrative, emissions are categorized into three scopes:
1) Scope 1 includes direct emissions from owned or controlled sources (like factory emissions).
2) Scope 2 covers indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy (like electricity used in operations).
3) Scope 3 encompasses all other indirect emissions, like those from the supply chain, employee commuting, and product use.
AI solutions: A Game-Changers in Manufacturing
An AI-driven solution , like BeChained’s, designed to eliminate wasted energy in manufacturing processes, whether for paper, metal, food & beverage, or chemicals is significant to reduce carbon emissions.
Here’s how it bridges the gap between theory and practice in carbon insetting:
1) Integration with Existing Systems: it smoothly integrates into existing manufacturing facilities. This seamless integration means there’s no need for a complete overhaul of current systems.
2) Continuous Optimization: The AI continuously monitors and identifies the optimal settings for machinery.
For instance, it can adjust the blade speed in a paper pulper or the pressure in a water pump to ensure maximum efficiency.
3) Automatic Execution: Once the AI identifies the best settings, it automatically implements these changes, ensuring that the production processes are always running at their optimal energy efficiency.
4) Direct Impact on Energy Consumption: By optimizing machinery settings, it directly reduces the amount of energy required for production. This not only cuts costs, but also lessens the reliance on energy resources that contribute to carbon emissions
5) Reducing Carbon Offsets: While the solution primary goal is to enhance efficiency (a form of carbon insetting), it also indirectly reduces the need for carbon offsetting.
By lowering the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes, less compensation via external projects is needed.
As well as it is key to make industrial manufacturers accountable of their carbon emissions. That is why it is important to track the carbon footprint and its reduction.
6) Sustainable Manufacturing: The result is a more sustainable manufacturing processes.
Companies using solution, like BeChained’s, not only save on energy costs, but also contribute to a healthier planet by significantly lowering their carbon emissions.
How the technology impacts on the Scopes
By doing this, such an AI-driven technology significantly impacts all the three Scopes:
Scope 1 (Integration and Continuous Optimization): By optimizing machinery settings in real-time, this solution effectively reduces Scope 1 emissions. This is achieved through the direct reduction of energy consumption in manufacturing processes.
Scope 2: Reduction in Energy Resources: As it enhances energy efficiency, it indirectly impacts Scope 2 emissions. Reduced energy demand means less reliance on external energy sources, which often contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Scope 3 (indirectly): While it primarily targets Scope 1 and 2 emissions, improved efficiency can ripple through the supply chain, potentially reducing Scope 3 emissions.
For instance, more efficient manufacturing processes can lead to lower energy requirements for suppliers. 19% in the case of BeChained solution.

Conclusion:
Solutions like BeChained represents a practical application of carbon insetting in the industrial sector, but with an impact even at govern side.
By making production processes more energy-efficient, it directly cuts down on the carbon emissions associated with energy consumption.
This approach not only benefits the environment, but also enhances the operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness of manufacturing facilities.
In a world increasingly conscious of its carbon footprint, especially at product level, solutions like BeChained are essential in steering industries towards a more sustainable impact for a greener future.